Introduction: Why Axis Configuration Matters in Modern Manufacturing
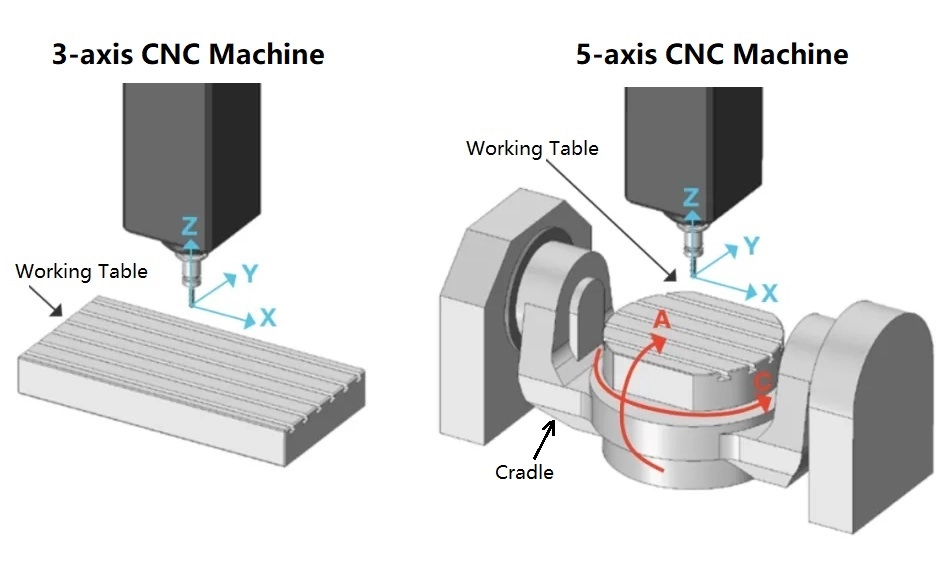
In CNC machining, the number of controlled axes directly determines what geometries can be produced, how accurately they can be manufactured, and how efficiently production can scale. When comparing 5 axis CNC vs. 3 axis CNC, the difference is not incremental—it fundamentally reshapes machining strategy, part quality, and total manufacturing cost.
While 3 axis CNC machining remains widely used for simple prismatic parts, 5 axis CNC machining has become critical for aerospace, medical, energy, and high-precision industrial applications where complex geometries, tight tolerances, and advanced materials are non-negotiable.
This article explains the key differences you should know, from motion capability and accuracy to cost justification and real-world use cases.
What Is 3 Axis CNC Machining?
3 axis CNC machining operates along three linear axes: X, Y, and Z. The cutting tool approaches the workpiece from a single direction, requiring multiple setups if features exist on different faces.
Characteristics of 3 Axis CNC Machining
-
Linear movement only (X, Y, Z)
-
Multiple fixtures required for multi-face parts
-
Higher risk of cumulative alignment error
-
Lower machine and programming cost
3 axis CNC machining is effective for flat surfaces, slots, holes, and basic housings. However, once geometry becomes contoured or multi-angled, its limitations become apparent.
What Is 5 Axis CNC Machining?
5 axis CNC machining adds two rotational axes (typically A and B or A and C) to the traditional three linear axes. This allows either the tool or the workpiece to tilt and rotate during cutting.
Core Capabilities of 5 Axis CNC Machining
-
Simultaneous machining from multiple angles
-
Single-setup manufacturing for complex parts
-
Shorter tool lengths and better rigidity
-
Continuous toolpath control
By enabling access to complex geometries in one setup, 5 axis CNC machining dramatically improves accuracy, surface finish, and production efficiency.
5 Axis CNC vs. 3 Axis CNC: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Parameter | 3 Axis CNC | 5 Axis CNC |
|---|---|---|
| Axis Movement | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z + 2 rotary axes |
| Setup Count | Multiple | Single (in most cases) |
| Geometric Complexity | Limited | Extremely high |
| Typical Tolerance | ±0.005" | ±0.0005" |
| Surface Finish | 1.6–3.2 µm Ra | <0.4 µm Ra |
| Tool Reach | Long tools required | Short, rigid tools |
| Programming Complexity | Low | High |
| Application Scope | General machining | Aerospace, medical, advanced parts |
This comparison highlights why 5 axis CNC machining is increasingly favored for complex parts manufacturing.
Accuracy and Tolerance: The Precision Gap
In high-stakes industries, tolerance stack-up from multiple setups is unacceptable. With 3 axis CNC machining, every re-fixturing introduces potential misalignment.
5 axis CNC machining eliminates this risk by maintaining datum integrity throughout the process. Continuous multi-axis tool control enables:
-
Micron-level geometric consistency
-
Improved positional accuracy
-
Superior repeatability across production batches
For aerospace brackets, turbine components, and orthopedic implants, this precision is not optional—it is mandatory.
Surface Finish and Tool Engagement
Surface quality is directly affected by tool angle and engagement consistency.
-
3 axis CNC machining often requires secondary finishing operations
-
5 axis CNC machining maintains optimal tool orientation throughout the cut
As a result, 5 axis CNC machining achieves surface finishes below 0.4 µm Ra, reducing polishing time and improving fatigue resistance in load-bearing parts.
Efficiency, Lead Time, and Cost Considerations
When 3 Axis CNC Makes Sense
-
Simple geometries
-
Low-volume or prototype work
-
Cost-sensitive projects with loose tolerances
When 5 Axis CNC Is Worth the Investment
-
Complex parts manufacturing
-
Tight tolerances and high surface requirements
-
Advanced materials like titanium and Inconel
-
Reduced lead time through single-setup machining
Although 5 axis CNC machines have higher upfront costs, total cost of ownership is often lower due to reduced setups, fewer fixtures, and lower scrap rates.
Industry Applications: Where the Difference Matters Most
Aerospace Manufacturing
5 axis CNC machining enables lightweight structural components, impellers, and turbine blades that are impossible to machine accurately on 3 axis systems.
Medical Device Manufacturing
Custom implants and surgical tools require smooth surfaces and complex organic shapes—ideal for 5 axis CNC machining.
Energy and Industrial Equipment
High-load components benefit from precise geometry and superior surface integrity delivered by 5 axis CNC machining.
Choosing Between 5 Axis CNC and 3 Axis CNC
The decision should be driven by part geometry, tolerance requirements, and long-term production strategy—not machine cost alone.
If your parts involve:
-
Multiple compound angles
-
Tight GD&T requirements
-
High-performance materials
Then 5 axis CNC machining is the correct technical choice.
FAQ
1. Is 5 axis CNC machining more accurate than 3 axis CNC machining?
Yes. 5 axis CNC machining reduces setup error and maintains consistent datums, resulting in significantly higher accuracy.
2. Why is 5 axis CNC machining critical for complex parts manufacturing?
It allows multi-face and contoured features to be machined in a single setup, improving precision and efficiency.
3. Is 3 axis CNC machining becoming obsolete?
No. 3 axis CNC machining remains effective for simple parts, but it cannot replace 5 axis CNC machining for complex geometries.
4. Does 5 axis CNC machining reduce production time?
Yes. Fewer setups, shorter tools, and optimized toolpaths significantly reduce total machining time.






